In this series

There was no shortage of biblical archaeology news in 2020, despite COVID-19 restrictions that canceled almost all of Israel’s scheduled excavations. Some limited digs still took place in Israel and surrounding countries, and research on previous excavations continued, resulting in some major announcements.
Here are 2020’s biggest stories about archaeology connecting us with the biblical world:
10. Assyrian god carvings
Italian and Kurdish archaeologists uncovered 15-foot rock carvings depicting an Assyrian king and seven Assyrian gods standing on the backs of sacred animals. The artwork was carved in relief in a cliff along a canal in the northern Kurdistan region of Iraq. The king is believed to be Sargon II, who ruled from 722 to 705 B.C. and conquered the northern kingdom of Israel (2 Kings 17:6). It is possible that the canal where the relief was found was dug by Israelites enslaved by Sargon II.
9. Church built on a solid rock
A dig in Banias in northern Israel has revealed the remains of a fourth-century church built, as was a common practice, atop a shrine to another god. Banias was a cultic center of worship of the god Pan, and the shrine was likely for worship of the Greek deity associated with sex and spring.
Christians in the fourth century, however, would have recognized the location as the biblical Caesarea Philippi, near the location where Peter told Jesus, “You are the Christ” and Jesus replied, “On this rock, I will build my church” (Matt. 16:13–19). One stone in the ruin is marked with cross etchings left by pilgrims who visited the church shortly after Christianity became the official religion of the Roman Empire.
8. Fort allied with King David
Archaeologists uncovered a fortified building in the Golan Heights dated to the time of David’s rule, about 1,000 B.C. A large basalt stone in the fortress is engraved with two horned figures with outstretched arms.
Archaeologists believe this building was an outpost of the kingdom of Geshur, an ally of King David. David’s wife Maacah, the mother of Absalom, was the daughter of the king of Geshur.
7. Holy smoke residue
A new test on organic remains on the burned surface of an eighth century B.C. altar revealed a residue of marijuana. This is the first evidence cannabis was associated with any form of worship in ancient Israel and the oldest known ritual use of marijuana to date. The altar was dedicated to the worship of the God of Abraham, Isaac, and Jacob.
The worship center at the desert stronghold of Arad was first excavated in the 1960s. Tests done half a century ago came back inconclusive. New tests were done using improved equipment and techniques. A second altar at the site carried traces of frankincense.
6. A temple to rival Jerusalem
Tel Aviv University archaeologists calculate that a temple, discovered during reconstruction of Israel’s Highway 1, near Jerusalem, was built around 900 B.C. The Motza temple is estimated to be similar in size to the temple built by Solomon a half-century earlier and just five miles to the east. The rival temple was likely used to worship the God who brought the Israelites out of Egypt—and other gods too.
The discovery was startling but fits well with the Old Testament narrative of national disputes over where, how, and who to worship. Scholars think some key Scriptural texts were composed as defenses of Jerusalem-based worship, and 1 Kings recounts how, during the same century, the northern kingdom of Israel constructed worship centers at Dan and Bethel.
5. Smiting gods of Canaan
Israeli archaeologist Yosef Garfinkel uncovered the ruins of a Canaanite temple from the 12th century B.C. The excavation site, located in Lachish, one of the most important Old Testament cities in the region, has yielded a trove of artifacts used in Canaanite worship, including jewelry, daggers, and two four-inch-tall bronze figurines of “smiting gods.”
Perhaps the most significant discovery at the temple is a bronze scepter coated with silver. Garfinkel believes it was held by a human-sized statue of the Canaanite god Baal. The statue itself was not found, but large statues of ancient Canaanite gods are rare.
4. Well-preserved palace
Archaeologists working on a road project in the Jezreel Valley outside the modern city of Afula discovered a royal complex that served Israelite kings such as Omri and Ahab. The complex is located just a half dozen miles from Tel Jezreel, site of another palace of King Ahab. A large pillared building they uncovered was described as “the best preserved building of the House of Omri ever found in Israel.” Storage jars found at the site reveal what appears to have been a centralized system of food distribution.
3. Church in a house at Laodicea
Turkish archaeologist Celal Şimşek discovered sacred items used in Christian worship while excavating a house in Laodicea. The peristyle house—built around a central garden or courtyard—was located next to a theater and was likely owned by wealthy people. The apostle Paul sent an epistle to the church at Laodicea, which is mentioned in Colossians but appears to have been lost. The church is also mentioned in Revelation, when Jesus condemns the Christians for saying, “I am rich; I have acquired wealth and do not need a thing,” when actually they are “wretched, pitiful, poor, blind, and naked” (Rev. 3:17).
Şimşek has not the detailed the religious items he unearthed, but concluded the house with a church will add to scholars’ understanding of “how Christianity spread in Laodicea since the middle of the first century.”
2. “Replica” is real; fragments are fake
One ongoing problem for biblical archaeologists is determining the authenticity of artifacts they don’t personally excavate—the items sold on the antiquities market. This year saw several major examples of how cutting-edge technology can help: A clay seal impression, once believed to be a forgery, was shown to be authentic, while fragments of the Dead Sea Scrolls, once believed real, were uncovered as fakes.
Ben Gurion University professor Yuval Goren and his team determined that a “bulla,” or clay seal, depicting a roaring lion, dates to the reign of Jeroboam II, who ruled from 788-748 B.C. It was purchased at a Bedouin market for a small sum a few decades ago.
At the same time, a firm that specializes in detecting art forgery discovered that 16 fragments of the Dead Sea Scrolls in the collection of the Museum of the Bible were all modern forgeries. The museum won praise for its thorough investigation and is now displaying the fakes with an exhibit focused on the problem of forgery. There are more than 70 other possibly faked fragments that have been offered to evangelical collectors since 2002.
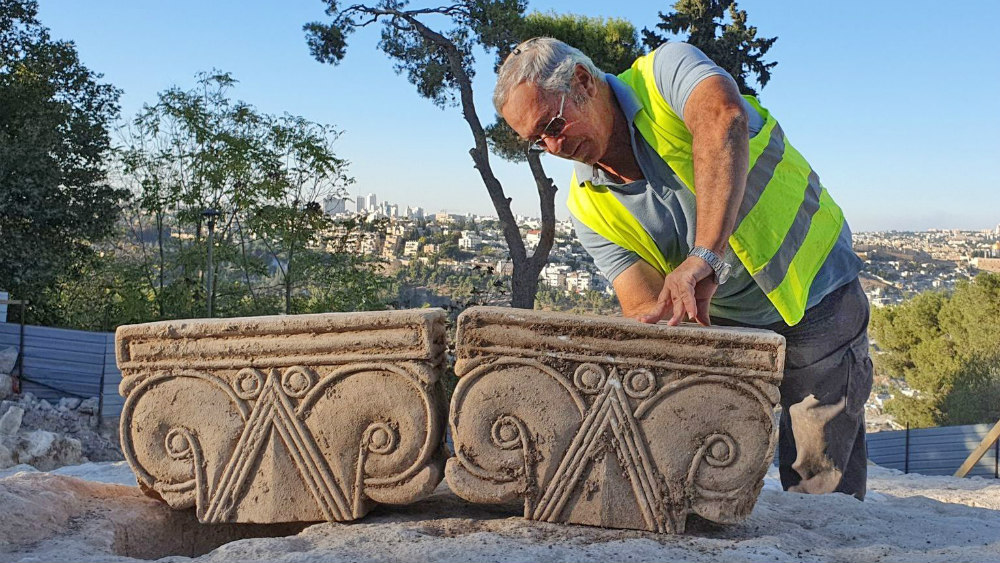
1. Remains of Manasseh’s reign
The discovery of the remains of a palace possibly belonging to King Manasseh, the ruler in 2 Kings 21 who “did much evil in the eyes of the Lord, provoking him to anger” and led the people to “do more evil than the nations had done that the Lord destroyed before the people of Israel,” dramatically expands archaeologists’ understanding of the reign of the later kings of Judah.
The ruins are located on the Armon Hanatziv promenade, a site that overlooks the Temple Mount and the Old City of Jerusalem from the south. The “proto-Aeolian” stonework is associated with royal buildings in the first temple period. The structure dates to the 55-year rulership of Manasseh, who took over the southern kingdom from his father King Hezekiah.
A few blocks away, near the newly constructed US embassy, archaeologists also found the remains of a large warehouse. It is believed to be a centralized food distribution facility and perhaps also served as storage for agricultural surplus. It dates from the same period.
A decade ago, archaeologists uncovered the remains of a palace and administrative center nearby in Ramat Rachel. This year’s publication of the report of the excavation, combined with the new digs, shows scholars that this area along the road to Bethlehem was a major center of activity for the later rulers of the kingdom of Judah.
Gordon Govier is editor of
, a quarterly biblical archaeology news magazine, and host of the weekly radio programThe Book & The Spade
.